Using payloads & wrapping out JSON parameters
SIA can process JSON payloads to fit into the individual needs of the user. The payloads can be used as a comparison in the Condition part of the mapping, as a value in the Custom value part of the mapping, or in the post-processing of an item
Condition example
This section will expand on how to use a single value from a payload as the condition for a mapping. This is useful when the user wants to utilize various parameters from a payload to trigger one or more mappings
We will be using this payload as the example:
{
"Value" : INT-value
}We want a mapping, where the condition specifies that the "Value" has to be 1 before we take any action
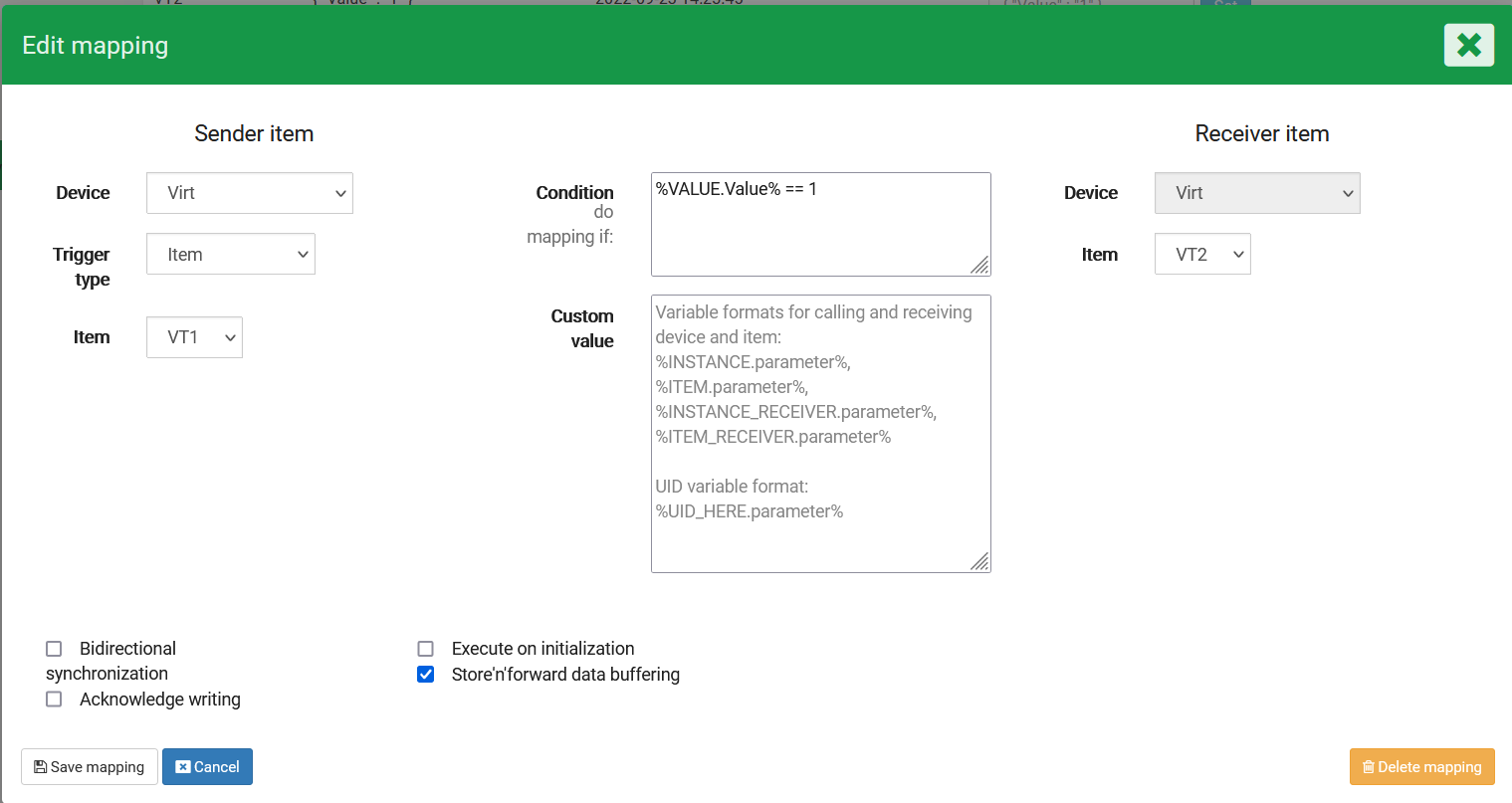
This way, if we send the payload:
{
"Value" : 1
}Then the mapping will trigger.
If the value is not 1, then the mapping will not trigger
Custom value example
We will use the same payload as before, but this time we will unwrap the value and send it to another item as the value. This is useful when you are reading payloads and want to send raw values to another instance/item
In the custom value of the mapping we will input %VALUE.Value% to get the raw value connected to this specific variable: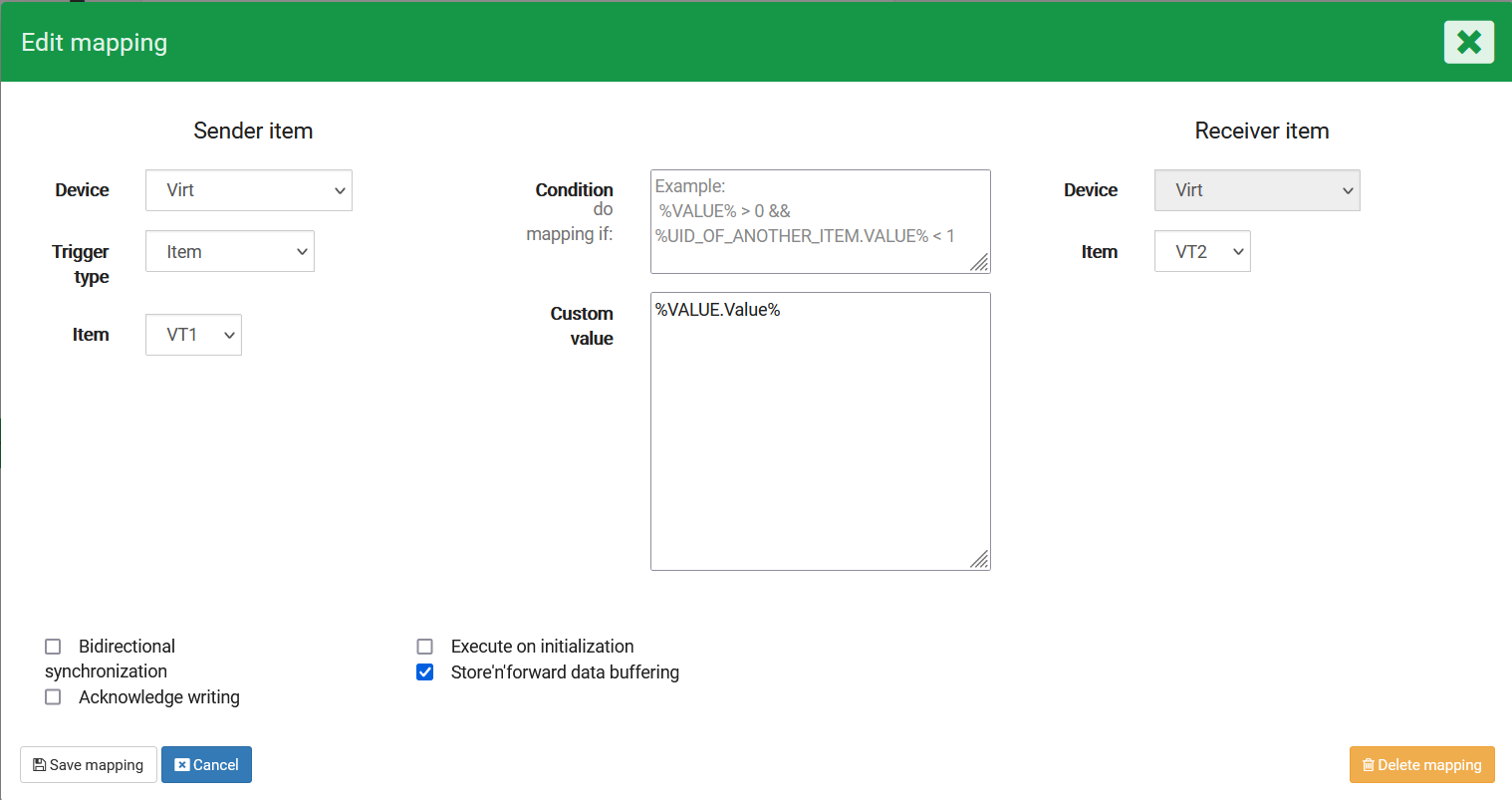
If we then input this payload in the sender item:
{
"Value" : 1
}We will see that the receiver item does not receive the full payload, but only the value connected to that variable:
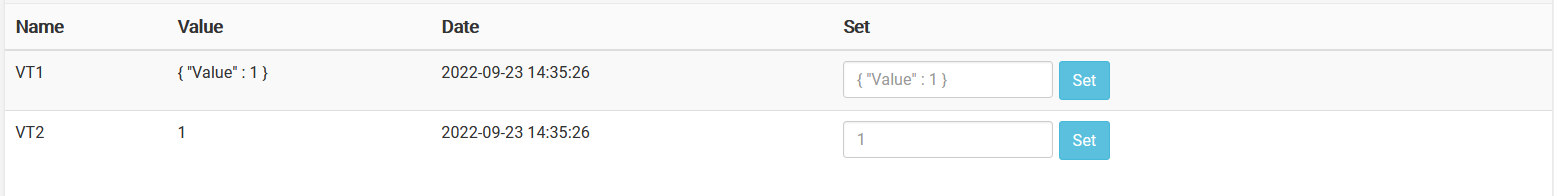
Post-processing example
A payload can be unwrapped and stored as the value of the item reading that payload. This is done by using the Post-Processing
We will be using the same example as before:
{
"Value" : 1
}In the Post-Processing of the item, we will input the following:
%VALUE.value%
The item should look like this:
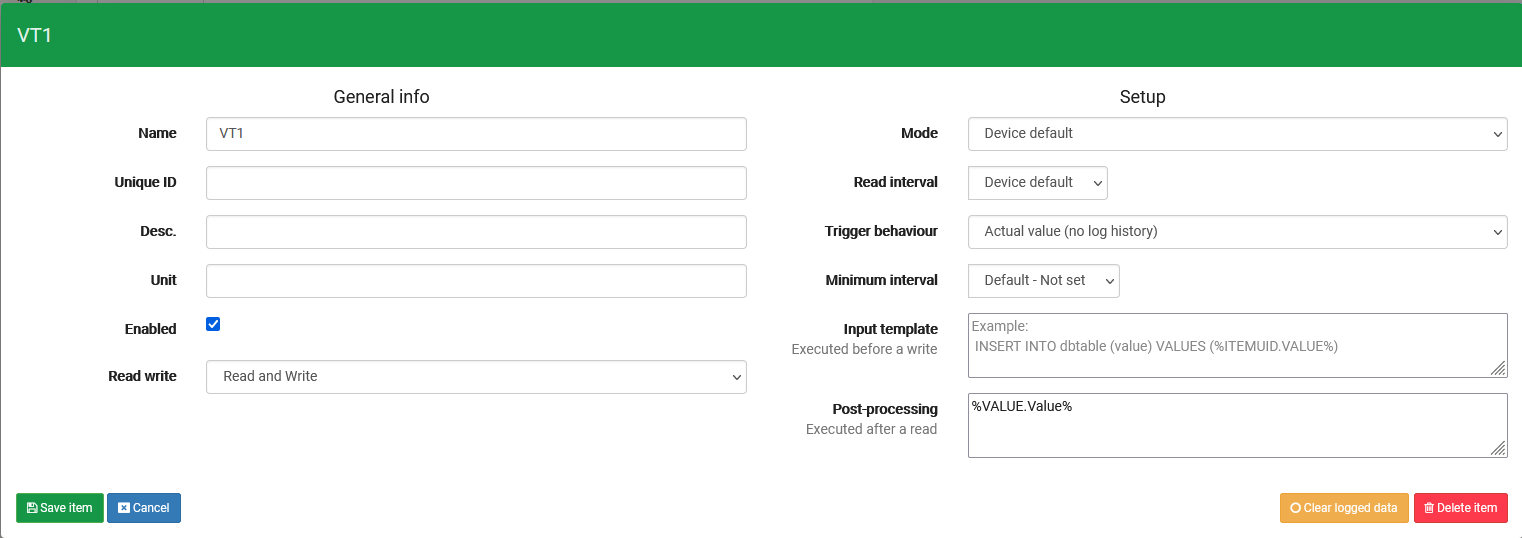
Our item is now only reading the INT-value from the value-variable:
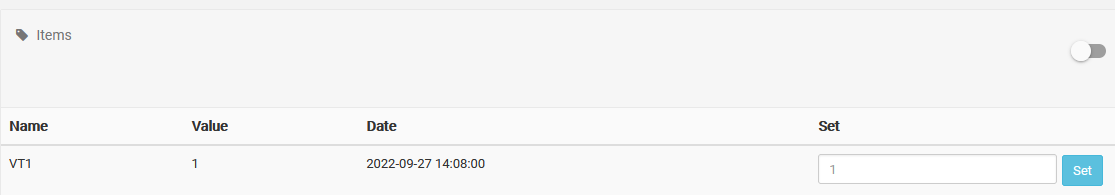
This method is especially useful when reading larger payloads, and the user only wants one specific piece of data
Payload and result examples
Below are some examples on how to unwrap specific values from specific payloads. The syntax will vary slightly, depending on how the payload is structured
| Payload | Payload example | User input |
Printed value |
|---|---|---|---|
| One object, one variable | { "value1":"1" } |
%VALUE.value1% | 1 |
| One object, many variables | { "value1":"1", "value2":"2", "value3":"3" } |
%VALUE.value2% | 2 |
| Array without objects |
["1","2","3"] |
%VALUE[0]% |
1 |
| Array with one object | [{ "value1": "1", "value2": "2", "value3": "3" }] |
%VALUE[0].value3% | 3 |
| Array with many objects | [{ "value1": "1" }, { "value2": "2" }, { "value3": "3" }] |
%VALUE[1].value2% | 2 |
| Array inside object | { "value1": "1", "value2": "2", "value3": [{ "valueX": "x", "valueY": "y" }] } |
%VALUE.value3[0].valueX% | x |